Because the Date and Time functions category has too many functions, I decide to break this blog post into different parts, so welcome to the second part!
Overview
Date and Time functions are used to perform a variety of operations over Dates, such as retrieving the current date and time or adding dates, etc. If you come from the BizTalk Server background or are migrating BizTalk Server projects, they are the equivalent of Date/Time Functoids inside BizTalk Mapper Editor.
Available Functions
The Date and Time functoids are:
- Add days: Adds a positive or negative number of days to the specified timestamp. Returns a timestamp that’s respectively later or earlier than the specified timestamp.
- Add DayTime to Date: Adds a positive or negative DayTime duration to the specified Date value (xs:date). Returns a Date that’s respectively after or before the specified Date.
- Add DayTime to DateTime: Adds a positive or negative DayTime duration to the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime). Returns a DateTime that’s respectively after or before the specified DateTime.
- Add DayTime to Time: Adds a positive or negative DayTime duration to the specified Time value (xs:time). Returns a Time that’s respectively after or before the specified Time. Durations that wrap around past midnight also return an earlier Time.
- Add YearMonth to DateTime: Adds a positive or negative YearMonth duration to the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime). Returns a DateTime that’s respectively after or before the specified DateTime.
- Adjust Date: Adjusts the specified Date value (xs:date) to the current or dynamic time zone.
- Adjust DateTime: Adjusts the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime) to the current or dynamic time zone.
- Adjust Time: Adjusts the specified Time value (xs:time) to the current or dynamic time zone.
- Current date: Returns the current date in YYYY-MM-DD format.
- Current DateTime value: Returns the current date and time in YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss format.
- Current time: Returns the current date and time in YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss format.
- DateTime: Creates and returns a DateTime value based on the specified Date and Time.
- Day from Date: Returns the day from the specified Date value (xs:date).
- Day from DateTime: Returns the day from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
- Equal Date: Returns true or false based on whether the specified Date values are equal.
- Equal DateTime: Returns true or false based on whether with the specified DateTime values are equal.
- Equal Day: Returns true or false based on whether the specified Day values (xs:gDay) are equal with the same starting time when the day values are in the same month and year.
- Equal Month: Returns true or false based on whether the specified Month values (xs:gMonth) have the same starting time when the month values are in the same year.
- Equal MonthDay: Returns true or false based on whether the specified MonthDay values (xs:gMonthDay) are equal with the same starting time when the day values are in the same year.
- Equal Time: Returns true or false based on whether the specified Time values are equal.
- Equal Year: Returns true or false based on whether the specified Year values (xs:gYear) have the same starting time.
- Equal YearMonth: Returns true or false based on whether the specified YearMonth values (xs:gYearMonth) are the same.
- Greater Date: Returns true or false based on whether the first Date value is later than the second Date value.
- Greater DateTime: Returns true or false based on whether the first DateTime value is later than the second DateTime value.
- Greater Time: Returns true or false based on whether the first Time value is later than the second Time value.
- Hours from DateTime: Returns the hours from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
- Hours from Time: Returns the hours from the specified Time value (xs:time).
- Less Date: Returns true or false based on whether the first Date value is earlier than the second Date value.
- Less DateTime: Returns true or false based on whether the first DateTime value is earlier than the second DateTime value.
- Less Time: Returns true or false based on whether the first Time value is earlier than the second Time value.
- Minutes from DateTime: Returns the minutes from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
- Minutes from Time: Returns the minutes from the specified Time value (xs:time).
- Month from Date: Returns the month from the specified Date value (xs:date).
- Month from DateTime: Returns the month from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
- Seconds from DateTime: Returns the seconds from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
- Seconds from Time: Returns the seconds from the specified Time value (xs:time).
- Subtract Dates: Returns the DayTimeDuration value (xs:dayTimeDuration) representing the elapsed time between the starting times for the specified Date values.
- Subtract DateTimes: Returns a DayTimeDuration value (xs:dayTimeDuration) representing the elapsed time between the specified DateTime values..
- Subtract DateTime from Date: Subtracts a positive or negative DayTime duration from the specified Date value (xs:date). Returns a Date that’s respectively before or after the specified Date..
- Subtract DateTime from DateTime: Subtracts a positive or negative DayTime duration from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime). Returns a DateTime that’s respectively before or after the specified DateTime.
- Subtract DateTime from Time: Subtracts a positive or negative Time duration from the specified Time value (xs:time). Returns a Time that’s respectively before or after the specified Time. A duration that wraps around past midnight also returns a later Time.
- Subtract Times: Returns a DayTimeDuration value (xs:dayTimeDuration) representing the elapsed time between the specified Time values, which are treated as times on the same date.
- Subtract YearMonth from Date: Subtracts a positive or negative YearMonth duration from the specified Date value (xs:date). Returns a Date that’s respectively before or after the specified Date.
- Subtract YearMonth from DateTime: Subtracts a positive or negative YearMonth duration from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime). Returns a DateTime that’s respectively before or after the specified DateTime.
- Time zone from Date: Returns the time zone from the specified Date value (xs:date).
- Time zone from DateTime: Returns the time zone from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
- Time zone from Time: Returns the time zone from the specified Time value (xs:time).
- Year from Date: Returns the year from the specified Date value (xs:date).
- Year from DateTime: Returns the year from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
DateTime
This function states that it will create and returns a DateTime value based on the specified Date and Time.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath function: dateTime(xs:date($arg1), xs:time($arg1))
- dateTime(xs:date($arg1), xs:time($arg1)) as xs:dateTime
Rules:
- The
$arg1 needs to be an xs:date in the following format yyyy-MM-DD or yyyy-MM-DDZ. - The
$arg2 needs to be an xs:time in the following format HH:mm:ss or HH:mm:ss-hh:mm.
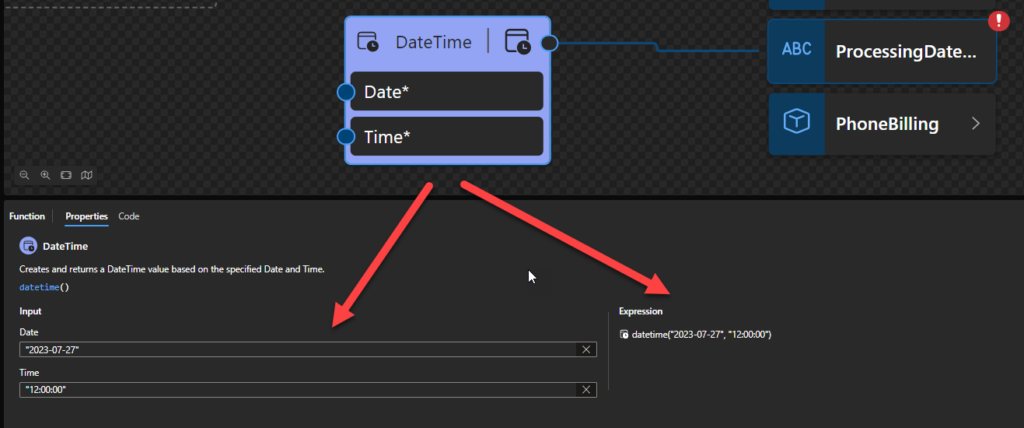
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: datetime(“2023-07-27”, “12:00:00”) will be translated to {dateTime(xs:date(‘2023-07-27′), xs:time(’12:00:00’))} and the return will be 2023-07-27T12:00:00
Day from Date
This function states that it will return the day from the specified Date value (xs:date).
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath function: day-from-date(xs:date($arg))
fn:day-from-date($arg as xs:date?)as xs:integer?
Rules:
- The function returns an
xs:integerbetween 1 and 31, both inclusive, representing the day component in the localized value of$arg. - The
$argneeds to be an xs:date in the following format yyyy-MM-DD or yyyy-MM-DDZ.
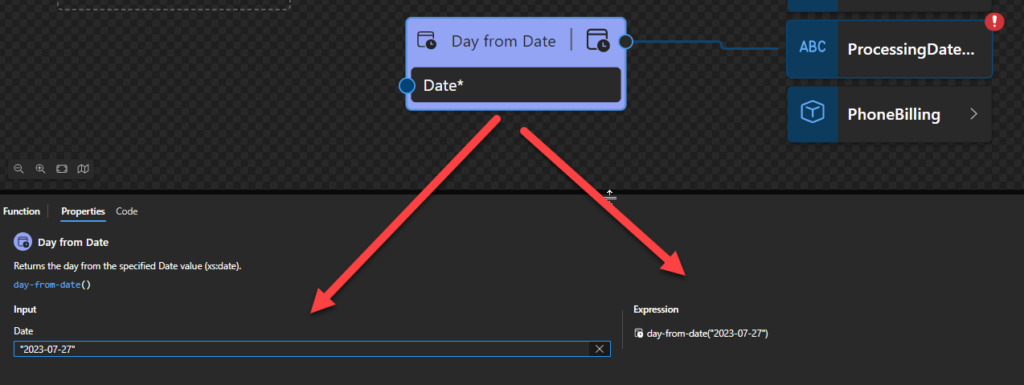
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: day-from-date(“2023-07-27”) will be translated to {day-from-date(xs:date(‘2023-07-27’))} and the return will be 27.
Day from DateTime
This function states that it will return the day from the specified DateTime value (xs:dateTime).
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath function: day-from-dateTime(xs:dateTime($arg))
fn:day-from-dateTime($arg as xs:dateTime?)as xs:integer?
Rules:
- The function returns an
xs:integerbetween 1 and 31, both inclusive, representing the day component in the localized value of$arg. - The
$argneeds to be an xs:dateTime in the following format yyyy-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss or yyyy-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss-hh:mm.
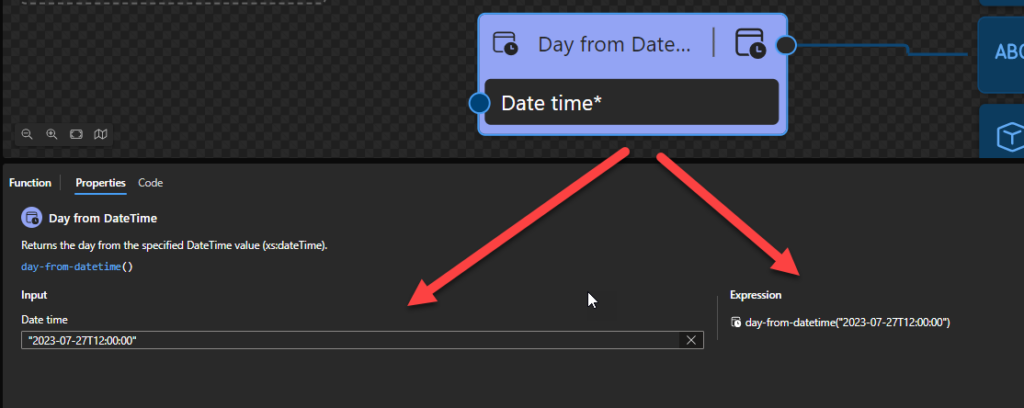
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: day-from-datetime(“2023-07-27T12:00:00”) will be translated to {day-from-dateTime(xs:dateTime(‘2023-07-27T12:00:00’))} and the return will be 27.
Equal Date
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether the specified Date values are equal.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:date($arg1) = xs:date($arg2)
- xs:date($arg1) = xs:date($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- The
$arg1 and $arg2 need to be an xs:date in the following format yyyy-MM-DD or yyyy-MM-DD-hh:mm
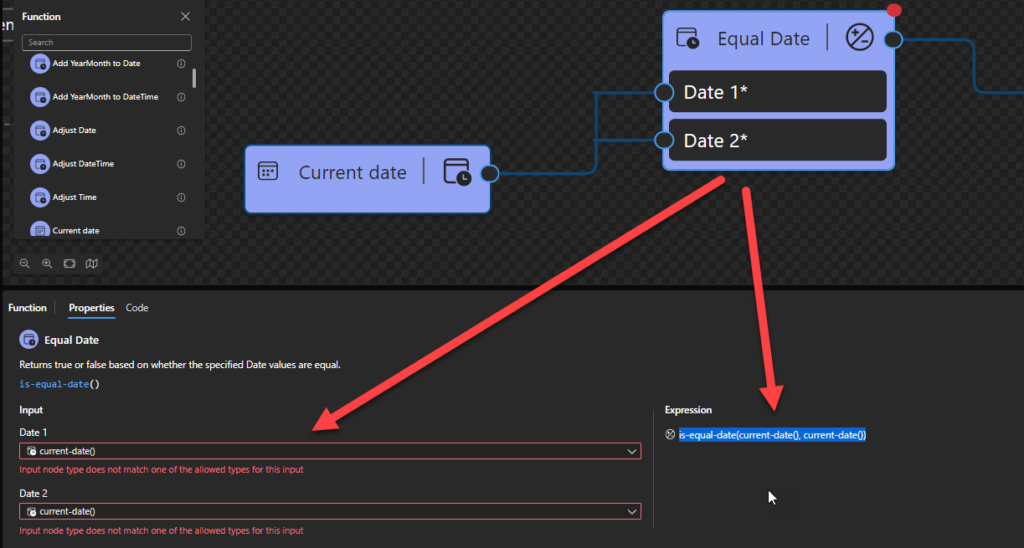
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-equal-date(current-date(), current-date()) will be translated to {xs:date(current-date()) = xs:date(current-date())} and the return will be true.
Equal DateTime
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether with the specified DateTime values are equal.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:dateTime($arg1) = xs:dateTime($arg2)
- xs:dateTime($arg1) = xs:dateTime($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- The
$arg1 and $arg2 need to be an xs:dateTime in the following format yyyy-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss or yyyy-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss-hh:mm.
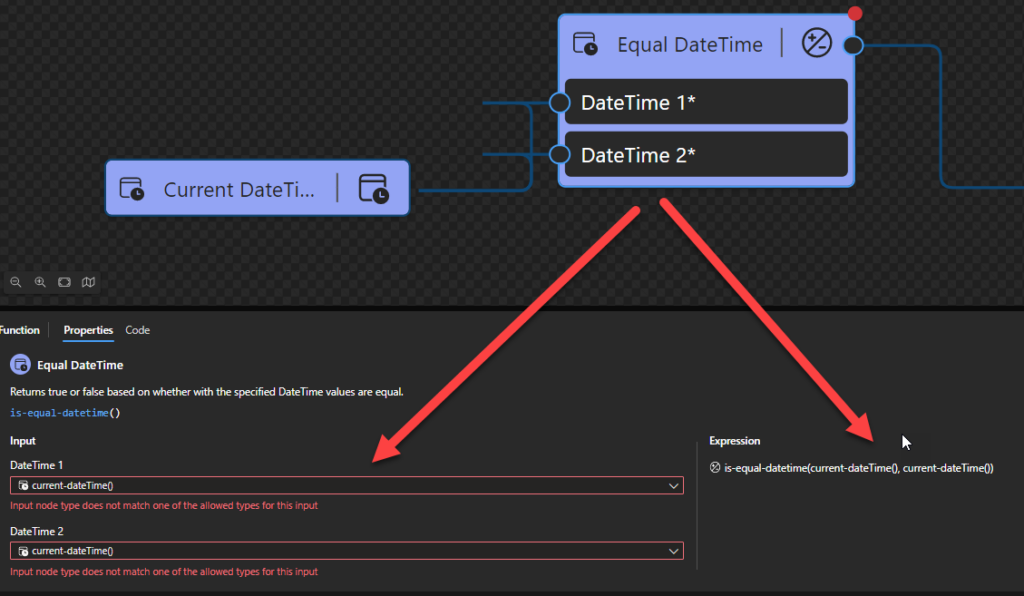
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-equal-datetime(current-dateTime(), current-dateTime()) will be translated to {xs:dateTime(current-dateTime()) = xs:dateTime(current-dateTime())} and the return will be true.
Equal Day
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether the specified Day values (xs:gDay) are equal with the same starting time when the day values are in the same month and year.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:gDay($arg1) = xs:gDay($arg2)
- xs:gDay($arg1) = xs:gDay($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- Returns true if the two
xs:gDayvalues (xs:gDay(“—25-14:00”)) have the same starting instant, when considered as days in the same month of the same year.
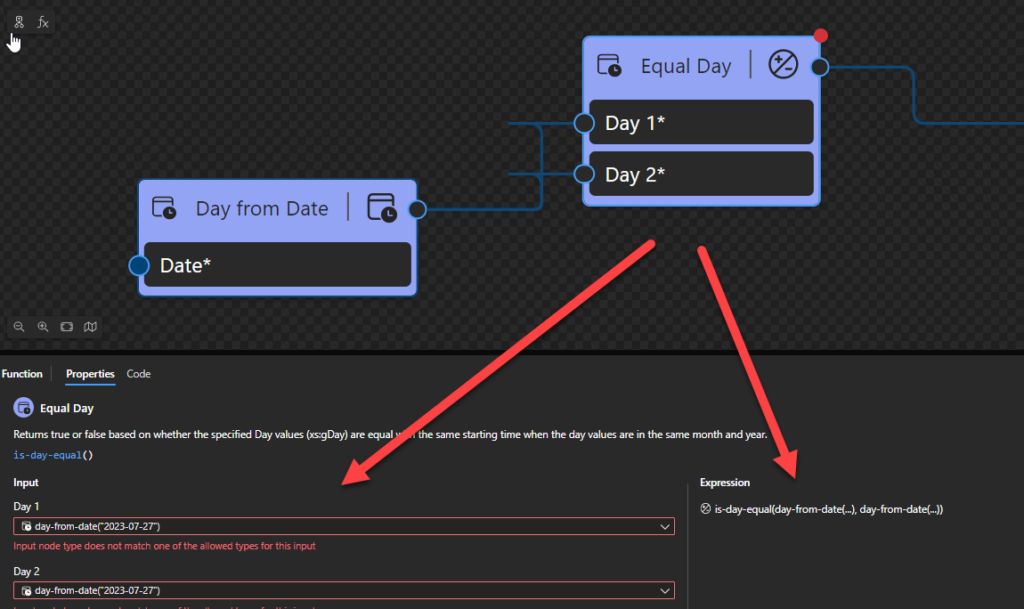
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-day-equal(day-from-date(…), day-from-date(…)) will be translated to xs:gDay(day-from-date(xs:date(‘2023-07-27’))) = xs:gDay(day-from-date(xs:date(‘2023-07-27’)))} and the return will be true.
Equal Month
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether the specified Month values (xs:gMonth) have the same starting time when the month values are in the same year.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:gMonth($arg1) = xs:gMonth($arg2)
- xs:gMonth($arg1) = xs:gMonth($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- Returns true if the two
xs:gMonthvalues (xs:gMonth(“–12-14:00”)) have the same starting instant, when considered as months in the same year.
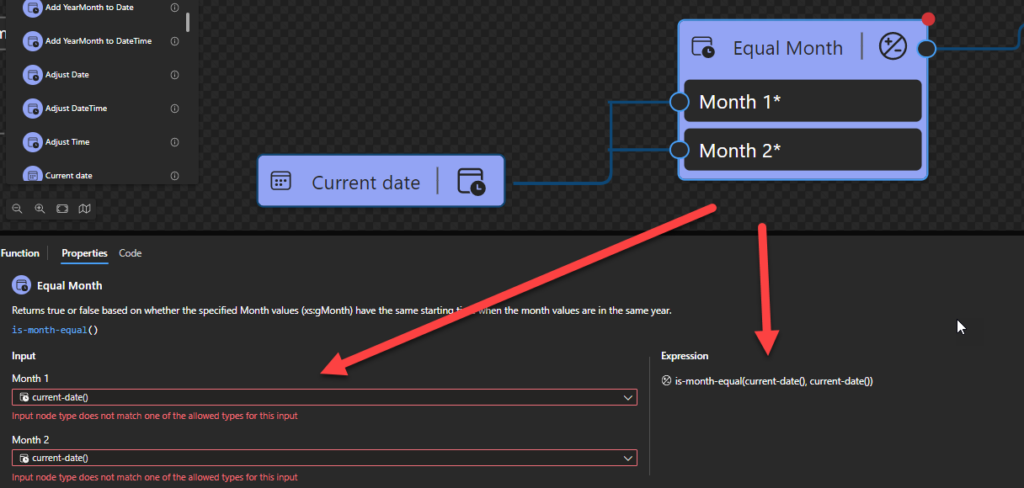
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-month-equal(current-date(), current-date()) will be translated to {xs:gMonth(current-date()) = xs:gMonth(current-date())} and the return will be true.
Equal MonthDay
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether the specified MonthDay values (xs:gMonthDay) are equal with the same starting time when the day values are in the same year.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:gMonthDay($arg1) = xs:gMonthDay($arg2)
- xs:gMonthDay($arg1) = xs:gMonthDay($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- Returns true if the two
xs:gMonthDayvalues (xs:gMonthDay(“–12-25-14:00”)) have the same starting instant, when considered as days in the same year.
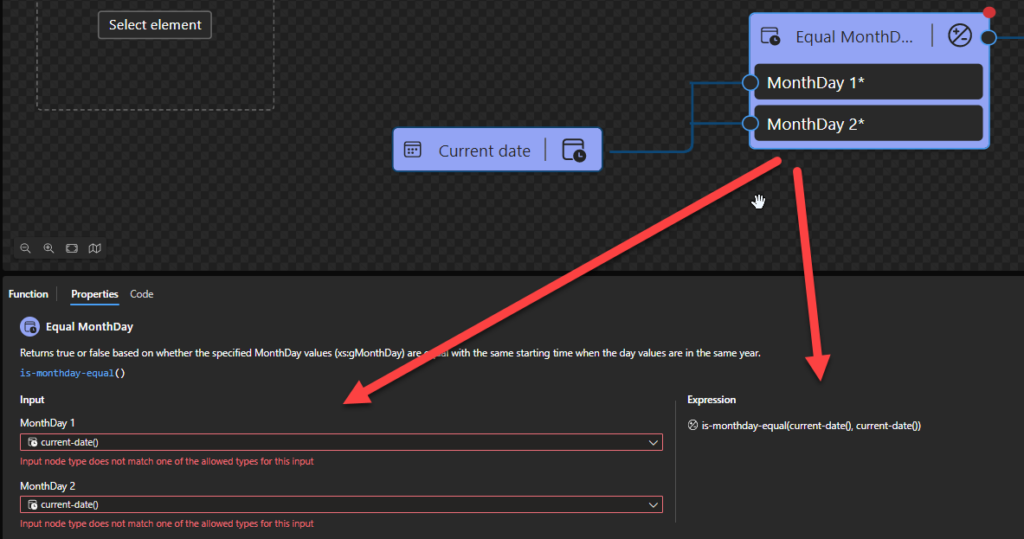
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-monthday-equal(current-date(), current-date()) will be translated to {xs:gMonthDay(current-date()) = xs:gMonthDay(current-date())} and the return will be true.
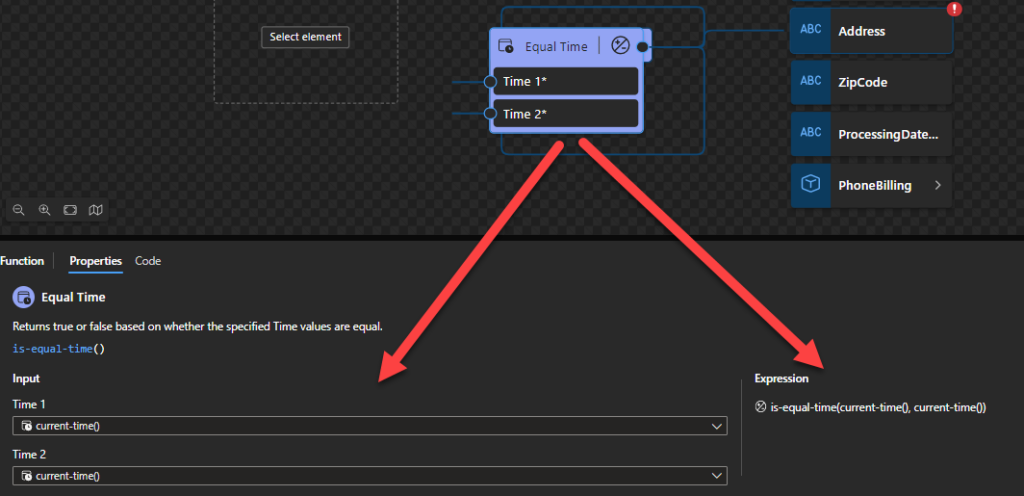
Equal Time
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether the specified Time values are equal.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:time($arg1) = xs:time($arg2)
- xs:time($arg1) = xs:time($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- Returns
trueif the twoxs:timevalues represent the same instant in time, when treated as being times on the same date, before adjusting the timezone.
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-equal-time(current-time(), current-time()) will be translated to xs:time(current-time()) = xs:time(current-time()) and the return will be true.
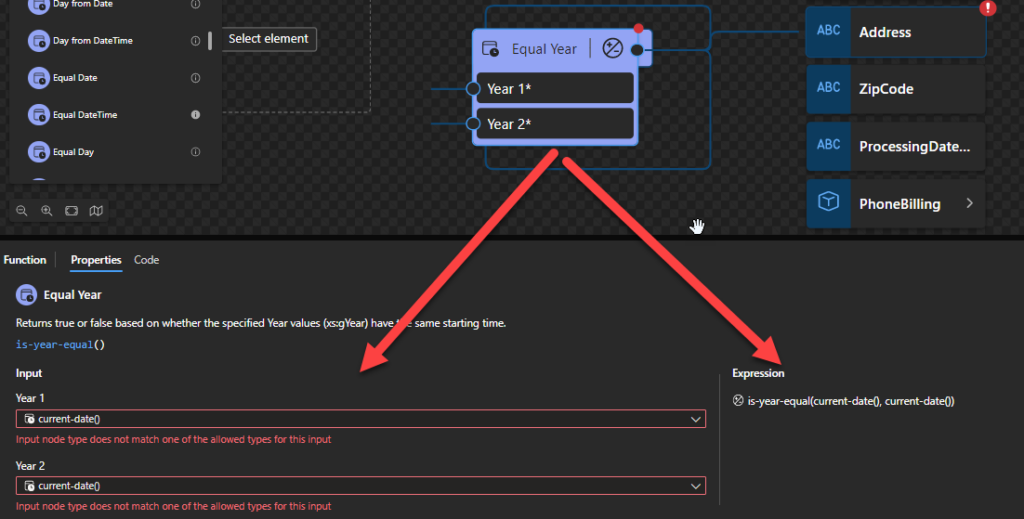
Equal Year
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether the specified Year values (xs:gYear) have the same starting time.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:gYear($arg1) = xs:gYear($arg2)
- xs:gYear($arg1) = xs:gYear($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- Returns true if the two
xs:gYearvalues (xs:gYear(“2005+12:00”)) have the same starting instant.
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-year-equal(current-date(), current-date()) will be translated to {xs:gYear(current-date()) = xs:gYear(current-date())} and the return will be true.
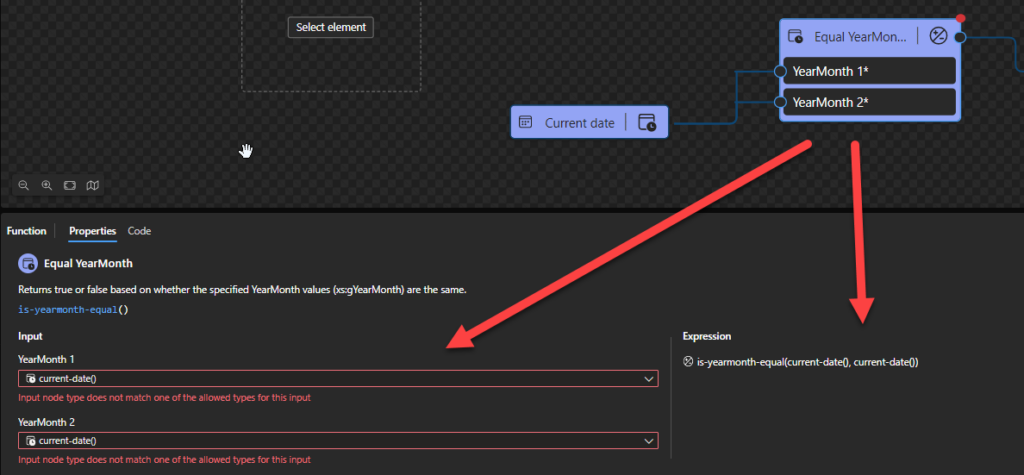
Equal YearMonth
This function states that it will return true or false based on whether the specified YearMonth values (xs:gYearMonth) are the same.
Behind the scenes, this function is translated to the following XPath expression: xs:gYearMonth($arg1) = xs:gYearMonth($arg2)
- xs:gYearMonth($arg1) = xs:gYearMonth($arg2) as xs:boolean
Rules:
- Returns true if the two
xs:gYearMonthvalues (xs:gYearMonth(“1986-02”)) have the same starting instant.
Sample:
- The following Data Mapper transformation rule: is-yearmonth-equal(current-date(), current-date()) will be translated to {xs:gYearMonth(current-date()) = xs:gYearMonth(current-date())} and the return will be true.
Stay tuned for the third part of this blog post.
Hope you find this helpful! So, if you liked the content or found it useful and want to help me write more, you can buy (or help buy) my son a Star Wars Lego!


